Antiracist economist Kim Crayton says that “intention without strategy is chaos.” We’ve discussed how our biases, assumptions, and inattention toward marginalized and vulnerable groups lead to dangerous and unethical tech—but what, specifically, do we need to do to fix it? The intention to make our tech safer is not enough; we need a strategy.
This chapter will equip you with that plan of action. It covers how to integrate safety principles into your design work in order to create tech that’s safe, how to convince your stakeholders that this work is necessary, and how to respond to the critique that what we actually need is more diversity. (Spoiler: we do, but diversity alone is not the antidote to fixing unethical, unsafe tech.)
The process for inclusive safety
When you are designing for safety, your goals are to:
- identify ways your product can be used for abuse,
- design ways to prevent the abuse, and
- provide support for vulnerable users to reclaim power and control.
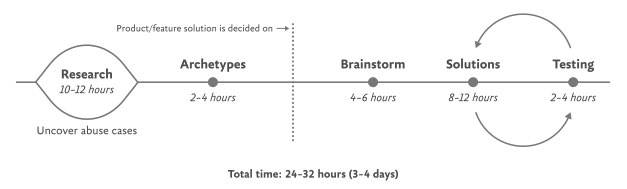
The Process for Inclusive Safety is a tool to help you reach those goals (Fig 5.1). It’s a methodology I created in 2018 to capture the various techniques I was using when designing products with safety in mind. Whether you are creating an entirely new product or adding to an existing feature, the Process can help you make your product safe and inclusive. The Process includes five general areas of action:
- Conducting research
- Creating archetypes
- Brainstorming problems
- Designing solutions
- Testing for safety
The Process is meant to be flexible—it won’t make sense for teams to implement every step in some situations. Use the parts that are relevant to your unique work and context; this is meant to be something you can insert into your existing design practice.
And once you use it, if you have an idea for making it better or simply want to provide context of how it helped your team, please get in touch with me. It’s a living document that I hope will continue to be a useful and realistic tool that technologists can use in their day-to-day work.
If you’re working on a product specifically for a vulnerable group or survivors of some form of trauma, such as an app for survivors of domestic violence, sexual assault, or drug addiction, be sure to read Chapter 7, which covers that situation explicitly and should be handled a bit differently. The guidelines here are for prioritizing safety when designing a more general product that will have a wide user base (which, we already know from statistics, will include certain groups that should be protected from harm). Chapter 7 is focused on products that are specifically for vulnerable groups and people who have experienced trauma.
Step 1: Conduct research
Design research should include a broad analysis of how your tech might be weaponized for abuse as well as specific insights into the experiences of survivors and perpetrators of that type of abuse. At this stage, you and your team will investigate issues of interpersonal harm and abuse, and explore any other safety, security, or inclusivity issues that might be a concern for your product or service, like data security, racist algorithms, and harassment.